Blockchain have many key purposes.
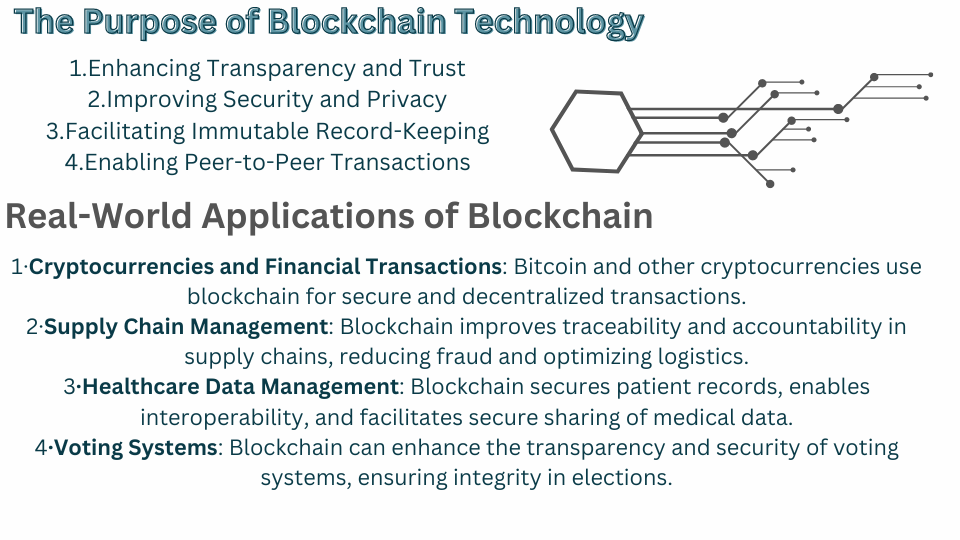
Enhancing Transparency and Trust.
this help to promotes its transparency and accuracy by providing a tamper-proof record of transactions. Each transaction is recorded and stored on a public ledger, which enabling the stakeholders to verify the data integrity without any intermediaries.
Improving Security and Privacy.
It help in cryptographic techniques to safe and secure the data, making it highly unavailable and resistant to tampering and type of fraud. This increases the privacy and protects the any sort of sensitive information.
Facilitating Immutable Record-Keeping.
It ensures that once the data is stored and recorded safely, it cannot be changed retroactively without any consensus from the network participants. This characteristics is important for maintaining the data integrity.
Enabling Peer-to-Peer Transactions.
It enables direct denoting the transactions without the any help of intermediaries like banks or payment processors. This decreases the costs and speeds up transactions.
Real-World Applications
Blockchain technology have many applications in various sectors:
- Cryptocurrencies and Financial Transactions: Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies use the blockchain for safe and secure data and also for decentralized transactions.
- Supply Chain Management: Blockchain improves the traceability and accountability in the supply chains, which decreases the fraud and optimizing the logistics.
- Healthcare Data Management: Blockchain also recorded and secure the patient records, and enables the interoperability, and also provide the secure sharing of medical data.
- Voting Systems: Blockchain also increases the accuracy and transparency and security of the voting systems, which ensure the self-esteem and integrity in any elections.
Advantages and Disadvantages
Advantages
It offers several advantages.
- Security: Cryptographic algorithms ensure data integrity and prevent unauthorized access.
- Efficiency: Direct peer-to-peer transactions streamline processes and reduce operational costs.
- Transparency: Public ledgers enable stakeholders to track transactions in real-time.
Disadvantages
However, blockchain also faces challenges.
- Scalability Issues: This networks can struggle to handle large transaction volumes efficiently.
- Energy Consumption: Proof-of-Work consensus mechanisms consume substantial energy, raising environmental concerns.
Future Outlook and Potential Developments
The future holds exciting possibilities:
- Emerging Trends: Non-fungible tokens (NFTs), decentralized finance (DeFi), and smart contracts are shaping the evolution of blockchain.
- Integration with IoT and AI: Blockchain is poised to integrate with IoT devices and AI algorithms, enabling automated and secure data transactions.
- Regulatory Challenges: Blockchain adoption faces regulatory hurdles, necessitating clear guidelines to foster mainstream acceptance.





Excellent article
Good